As an essential component in the digital transformation of companies, Wide-Area Networks (WAN) must evolve to become resilient, scalable and secure architectures, and thus respond to the necessary changes in networks. Growing digital needs, a democratization of cloud usages: the last few years have seen the emergence of new connectivity technologies, offering ever more controlled quality of service and increasingly minimized service interruptions.
Today, let’s take a look at SD-WAN, a recent evolution in connectivity technologies.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide-Area Network) is a software-based approach to managing a WAN. It virtualizes a network link through the aggregation of multiple connectivity solutions. It has been touted in recent years as the next big thing in telecommunications.
SD-WAN allows for greater flexibility by separating the physical part of the network from its control and management planes. This approach has several key benefits:
- Increased resiliency, through the multiplication and diversification of link types, and intelligent routing;
- A pragmatic operational cost structure, as bandwidth can be increased via less expensive connectivity options such as Internet access or 3G/4G;
- Link security via next generation firewall (NGFW) equipment;
- A global visibility of the network and an increased agility on evolutions.
Initially, the technology was presented as a way to save bandwidth, thanks in particular to the intelligent routing of different types of traffic on a network. Today, the main benefit put forward by users and manufacturers is the optimization of the availability and latency perception of applications, allowing a better user experience.
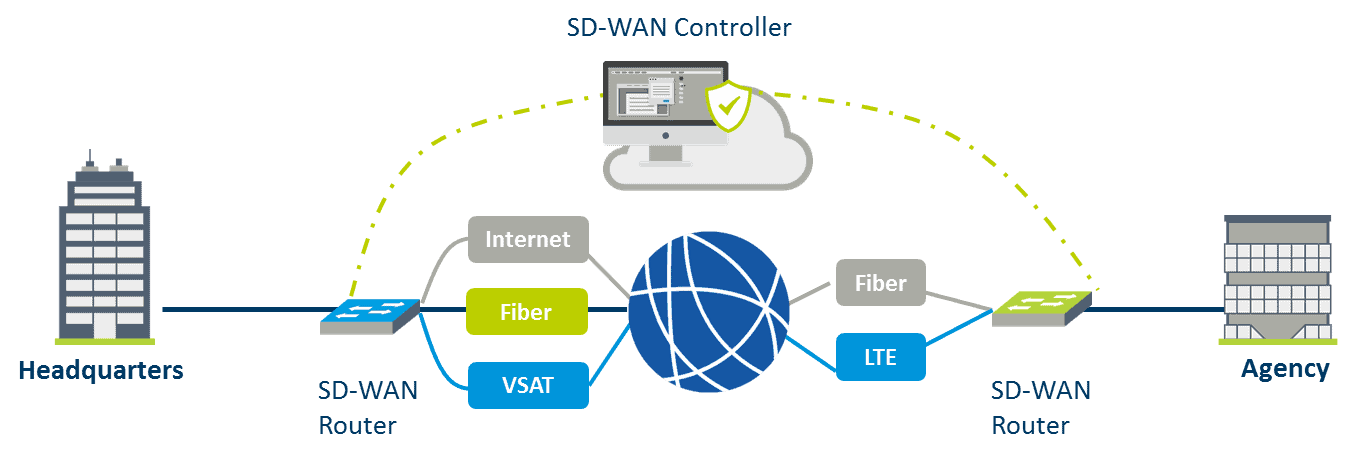
How does it work?
This technological approach therefore promises many improvements in service quality. But how does the technology work in practice?
Good planning is the key to good operations
First of all, the customer’s needs must be accurately defined. Depending on the network topology, the connectivity options available on site and the specificities of the applications used, the approaches will be different.
The first step is to accurately assess the customer’s business case; the returns on investment will not necessarily be the same depending on the use.
Mapping network traffic
Once this business case has been established, the careful planning phase can start, by communicating with the client and carrying out a site survey to identify the various sources of network traffic. It becomes then possible to classify the criticality of each network flow, in order to prioritize them.
The equipment
Specific equipment is required at both interconnection points: typically, an appliance (physical or virtual) will be installed at the receiving end, at the customer’s site, and another one, which will manage the other end of the connection, is installed in a datacenter, in the case of a centralized architecture of the customer, or on all or part of the client’s network sites.
Many vendors provide many different features; for example, Fortinet offers solutions integrated with a whole ecosystem oriented towards security, or Aruba (formerly Silverpeak) is more oriented towards flow optimization.
Connectivity
It is now necessary to connect these two endpoints together. All types of connections are compatible here, and this is what makes this technology special: the flows will be routed on the link offering the necessary characteristics for a specific stream. One of the important steps will be to set up the SD-WAN appliances by defining the desired SLAs for intelligent traffic routing. For example, real-time applications, where latency and/or jitter are critical and should ideally be kept to a minimum, will be routed over the link offering the right characteristics. In the case of a critical application, it is even possible to transmit the data twice, on two separate links, to ensure that if one of the two links were to be degraded, the data would still reach its destination.
What result?
Through careful and well-prepared deployment, increased quality of service and connection stability is achieved while minimizing service interruptions. This quality is also achieved without the need for costly bandwidth increases to the primary link.
These technologies act in a completely transparent way for the end user: sudden degradation or disconnection on a network link will have no impact on the data stream. Dynamic routing or load balancing, which balance the network load on several links, would fail altogether if one of the links suddenly disconnect.
What are the benefits of using SD-WAN?
The potential benefits of SD-WAN are numerous, and by extension so are its business cases.
Availability of critical applications
If your business depends on a remote application, whether it is a business application or a cloud application, SD-WAN can improve its availability, by allowing automatic switching between various links depending on their characteristics. If your application is sensitive to latency, jitter, or even just available bandwidth, SD-WAN can ensure that it is always prioritized, even if one of your links goes down, to improve the user experience.
Optimizing access to Microsoft Cloud Services
Some SD-WAN solutions can improve access to cloud services like Microsoft 365 or Azure. They detect Microsoft points of presence to route traffic to the edge points closest to the user, thereby reducing latency and/or jitter to ensure the best application performance.
Bandwidth optimization
If your application sometimes requires occasional bursts of extra bandwidth, SD-WAN can, for example, “overflow” your traffic onto a secondary link to keep your application connected. This allows you to benefit from very high availability VSAT connectivity, as well as an MPLS, fiber or terrestrial ADSL link for occasional bandwidth needs, in addition to VSAT.
Secure connectivity
The use of applications, especially in the cloud, requires a high level of security. SD-WAN meets this need through permanent security and encryption, by implementing anti-virus and anti-spam solutions, intrusion prevention and detection (IDS/IPS), application filtering and through complete control of the authentication process.
When not to use SD-WAN?
The use of SD-WAN is evaluated on a case-by-case basis: depending on the characteristics of the links available between the points to be connected and your needs, SD-WAN can improve the quality of service for your network applications. However, SD-WAN is not suited for all networks; there are several factors to consider in determining whether or not SD-WAN will benefit you.
One of the key factors in choosing SD-WAN is the variety of link types available between your two networks to be connected: the greater the variety, the more SD-WAN makes sense. Coupling Internet bandwidth to an MPLS or VSAT link, to minimize service interruptions and match bandwidth capacity requirements, will always be more economical. SD-WAN will allow you to intelligently route all your traffic in an optimal, secure and more cost effective way than by purchasing more bandwidth on your main link.
A large swath of new solutions are becoming available, such as low earth orbit (LEO) satellite fleets, 5G in large cities, or the deployment of new submarine cables. SD-WAN will allow you to use these new technologies alongside your existing links, in order to increase their bandwidth and availability, in a transparent way, but also to completely change their architecture: a network, today in MPLS, can be turned into a 100% Internet network.
The increase in the use of cloud solutions is also a critical factor: the more your applications are hosted in the cloud, the more important it is to be connected to them at all times. The resiliency of SD-WAN means that you can always be connected, no matter what happens, as multiple channels are used to connect your applications to your network.
Finally, there is a cost factor to consider: an increase in bandwidth may be sufficient for your needs, although diversifying links will always bring a benefit in terms of resilience to outages.
It is therefore necessary to carefully prepare an audit of your existing network, define your needs and carry out an expert evaluation by network engineers who will be able to precisely direct your connectivity needs and set up an evolution path.
Want To Know More?
Sonema has been provding connectivity services to its customers for 30 years, whether VSAT or terrestrial. We also offer a range of associated services to secure connectivity and improve network performance, such as SD-WAN. For more information, contact us.
